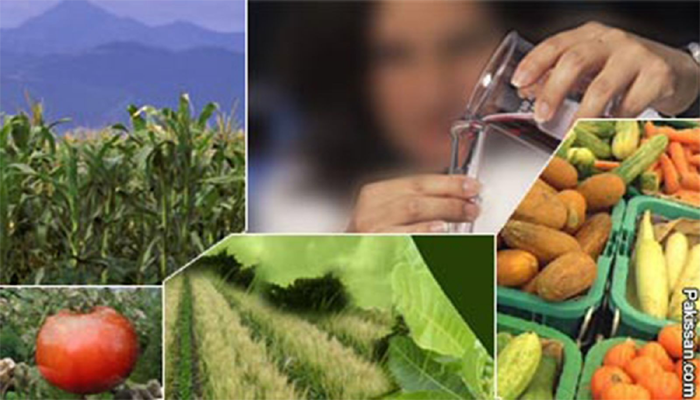
In recent decades, biotechnology has emerged as a powerful tool in agriculture, transforming the way we grow, harvest, and utilize crops. This innovative approach combines biology and technology, offering solutions to address the challenges of a growing global population, climate change, and resource limitations. Biotechnology in agriculture holds the promise of increased crop yields, improved nutritional content, and environmentally sustainable practices.
Genetically Modified Crops: Enhancing Resilience and Yield
One of the most significant applications of biotechnology in agriculture is the development of genetically modified (GM) crops. Genetic modification involves the introduction of specific genes into the DNA of plants to confer desirable traits, such as resistance to pests, diseases, or environmental stressors. This process has led to the creation of crops with enhanced resilience and increased yields.
For example, Bt cotton, a genetically modified variety, produces a toxin that acts as a natural insecticide, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Similarly, drought-resistant crops are being developed to thrive in regions with water scarcity, ensuring more reliable harvests in challenging environmental conditions.
Precision Farming: Targeted and Efficient Agriculture
Biotechnology has also played a pivotal role in the rise of precision farming, which involves using technology to optimize crop yields while minimizing waste. Advances in biotechnology, coupled with data analytics and sensors, allow farmers to make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and fertilization. This targeted approach not only increases efficiency but also reduces the environmental impact of agricultural practices.
Nutritional Enrichment: Biofortification for Healthier Diets
Beyond improving yields, biotechnology is addressing global nutritional challenges through biofortification. Scientists are developing crops with enhanced nutritional content to combat deficiencies in vital nutrients. Golden Rice, for instance, is engineered to produce beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A. This biofortified crop aims to combat vitamin A deficiency, a significant health concern in many developing countries.
Environmental Sustainability: Reduced Chemical Usage
Biotechnology has the potential to make agriculture more sustainable by reducing the reliance on chemical inputs. Pest-resistant crops, for example, can minimize the need for chemical pesticides, leading to decreased environmental pollution and protecting non-target species. This shift towards more sustainable farming practices aligns with the growing global emphasis on eco-friendly and organic agriculture.
Challenges and Concerns: Navigating Ethical and Environmental Issues
While biotechnology in agriculture offers promising solutions, it is not without its challenges and concerns. Ethical considerations, potential impacts on biodiversity, and public skepticism require careful navigation. Striking a balance between technological innovation and ethical responsibility is crucial to ensuring the responsible deployment of biotechnology in agriculture.
Conclusion: A Greener, More Food-Secure Tomorrow
Biotechnology in agriculture holds immense potential to address the complex challenges facing global food production. By enhancing crop resilience, optimizing farming practices, and improving nutritional content, biotechnology contributes to building a more sustainable and food-secure future. As we continue to advance in this field, it is essential to prioritize ethical considerations, environmental sustainability, and inclusive dialogue to harness the full benefits of biotechnology in agriculture.